library system
Source URL: https://github.com/msa-ez/example-library
It is a management system for a library for book rental, reservation, and so on.
Repository
5 total
1. https://github.com/Juyounglee95/bookRental
2. https://github.com/Juyounglee95/gateway
3. https://github.com/Juyounglee95/bookManagement
4. https://github.com/Juyounglee95/point
5. https://github.com/Juyounglee95/view
service scenario
· Functional requirements
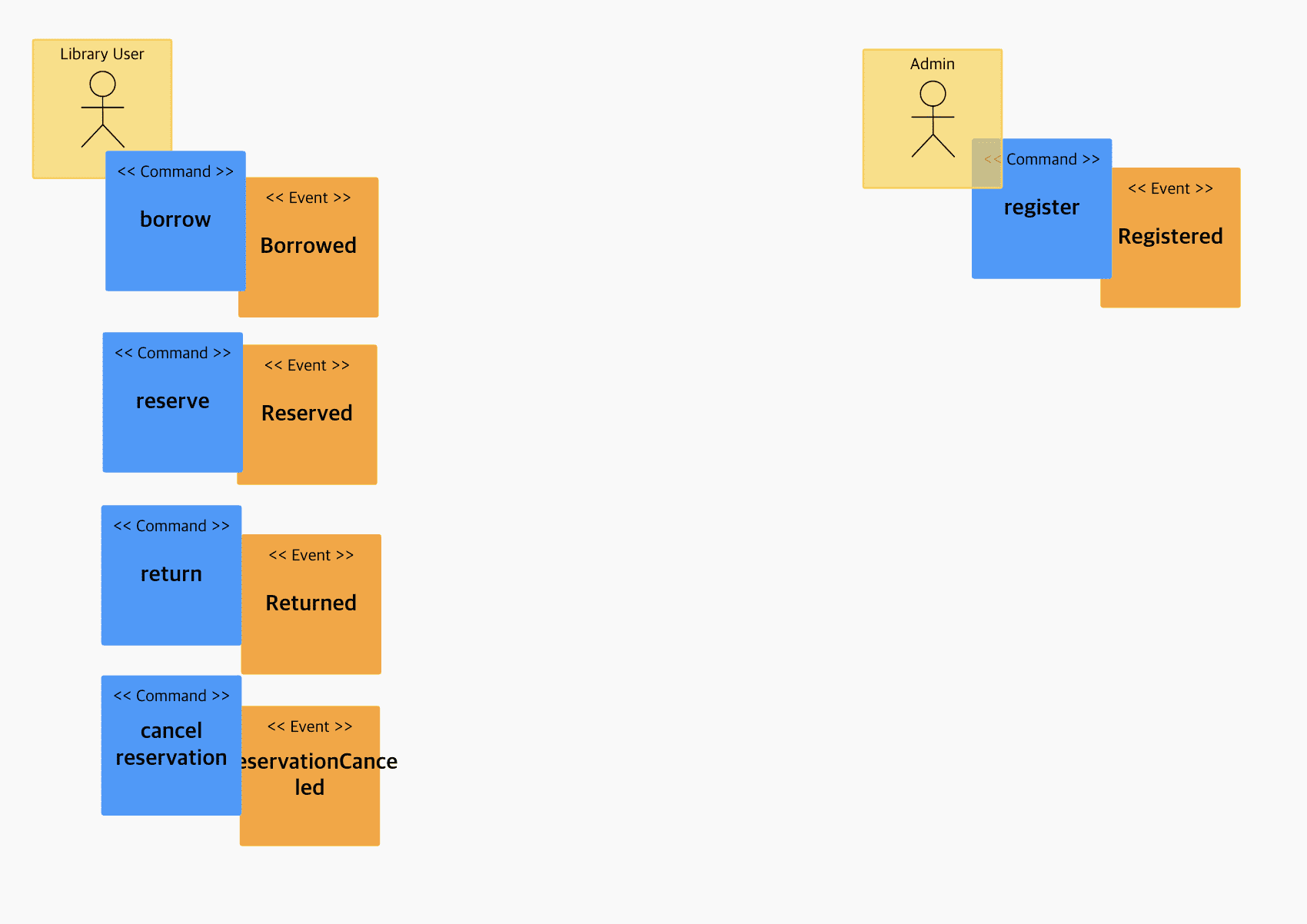
- The administrator registers the book.
- The user reserves the book.
- Points are used to reserve books. 3-1. Points will be returned in case of cancellation of reservation.
- The user returns the book.
· Non-functional requirements
-
transaction
- If payment is not made, it cannot be rented. Sync call
-
fault isolation
- Even if the library management function is not performed, rental/reservation should be available 24 hours a day, 365 days a year Async (event-driven), Eventual Consistency
- When the payment system is overloaded, it induces users to pay after a while without receiving them for a while Circuit breaker, fallback
- Performance Users should be able to check the status of the entire book by checking the entire book list. CQRS
checkpoint
- analytical design
-
Event Storming:
- Do you properly understand the meaning of each sticker color object and properly reflect it in the design in connection with the hexagonal architecture?
- Is each domain event defined at a meaningful level?
- Aggregation: Are Commands and Events properly grouped into ACID transaction unit Aggregate?
- Are functional and non-functional requirements reflected without omission?
-
Separation of subdomains, bounded contexts
-
Is the sub-domain or Bounded Context properly separated according to the team's KPIs, interests, and different distribution cycles, and is the rationality of the separation criteria sufficiently explained?
- Separation of at least 3 services
- Polyglot design: Have you designed each microservice by adopting various technology stack and storage structures according to the implementation goals and functional characteristics of each microservice?
- In the service scenario, for the use case where the ACID transaction is critical, is the service not excessively and densely separated?
-
-
Context Mapping / Event Driven Architecture
- Can you distinguish between task importance and hierarchy between domains? (Core, Supporting, General Domain)
- Can the request-response method and event-driven method be designed separately?
- Fault Isolation: Is it designed so that the existing service is not affected even if the supporting service is removed?
- Can it be designed (open architecture) so that the database of existing services is not affected when new services are added?
- Is the Correlation-key connection properly designed to link events and policies?
-
Hexagonal Architecture
- Did you draw the hexagonal architecture diagram according to the design result correctly?
-
Implementation
-
[DDD] Was the implementation developed to be mapped according to the color of each sticker and the hexagonal architecture in the analysis stage?
- Have you developed a data access adapter through JPA by applying Entity Pattern and Repository Pattern?
- [Hexagonal Architecture] In addition to the REST inbound adapter, is it possible to adapt the existing implementation to a new protocol without damaging the domain model by adding an inbound adapter such as gRPC?
- Is the source code described using the ubiquitous language (terms used in the workplace) in the analysis stage?
-
Implementation of service-oriented architecture of Request-Response method
- How did you find and call the target service in the Request-Response call between microservices? (Service Discovery, REST, FeignClient)
- Is it possible to isolate failures through circuit breakers?
-
Implementing an event-driven architecture
- Are more than one service linked with PubSub using Kafka?
- Correlation-key: When each event (message) processes which policy, is the Correlation-key connection properly implemented to distinguish which event is connected to which event?
- Does the Message Consumer microservice receive and process existing events that were not received in the event of a failure?
- Scaling-out: Is it possible to receive events without duplicates when a replica of the Message Consumer microservice is added?
- CQRS: By implementing Materialized View, is it possible to configure the screen of my service and view it frequently without accessing the data source of other microservices (without Composite service or join SQL, etc.)?
-
-
polyglot programming
- Are each microservices composed of one or more separate technology stacks?
- Did each microservice autonomously adopt its own storage structure and implement it by selecting its own storage type (RDB, NoSQL, File System, etc.)?
-
API Gateway
- Can the point of entry of microservices be unified through API GW?
- Is it possible to secure microservices through gateway, authentication server (OAuth), and JWT token authentication?
-
operation
-
SLA Compliance
- Self-Healing: Through the Liveness Probe, as the health status of any service continuously deteriorates, at what threshold can it be proven that the pod is regenerated?
- Can fault isolation and performance efficiency be improved through circuit breaker and ray limit?
- Is it possible to set up an autoscaler (HPA) for scalable operation?
- Monitoring, alerting:
-
Nonstop Operation CI/CD (10)
- When the new version is fully serviceable through the setting of the Readiness Probe and rolling update, it is proved by siege that the service is converted to the new version of the service.
- Contract Test: Is it possible to prevent implementation errors or API contract violations in advance through automated boundary testing?
-
Analysis/Design
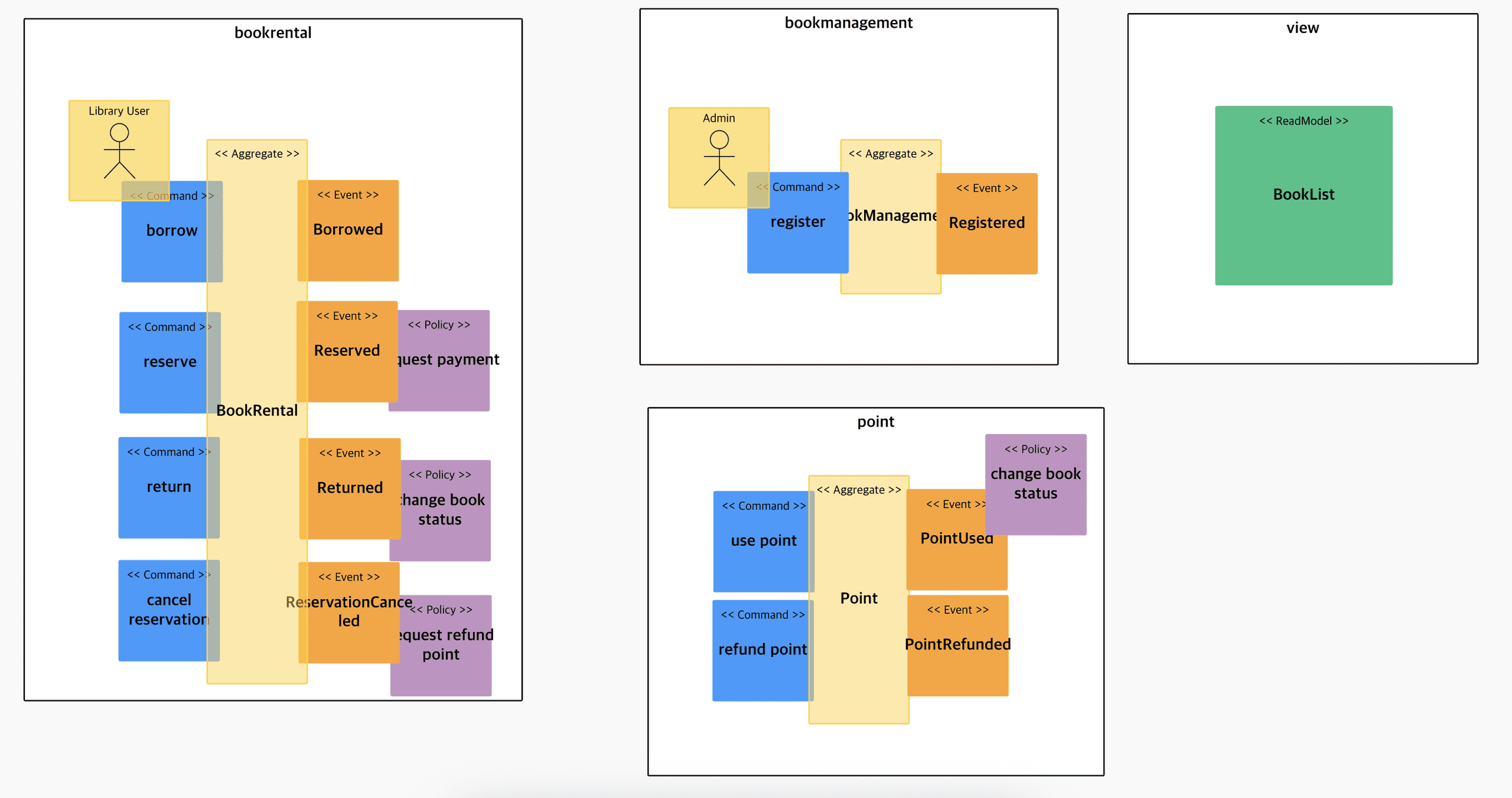
event derivation
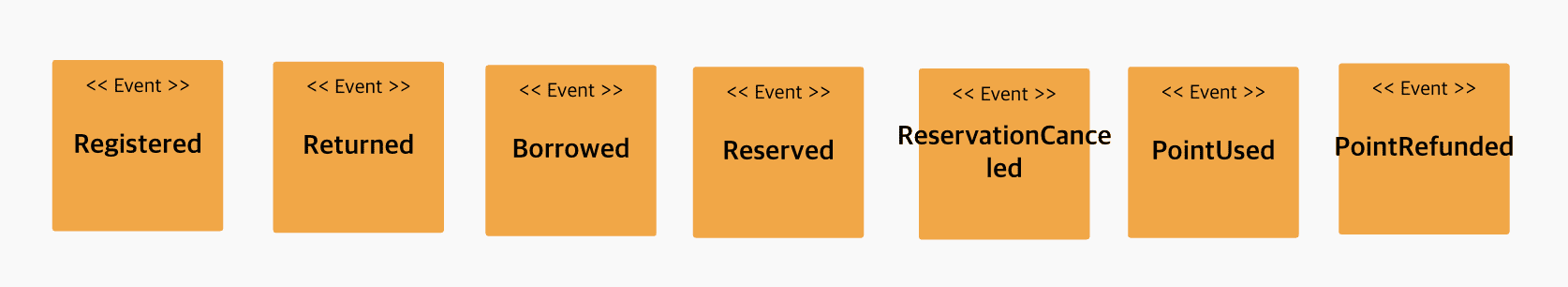
Attaching actors and commands to be read easily
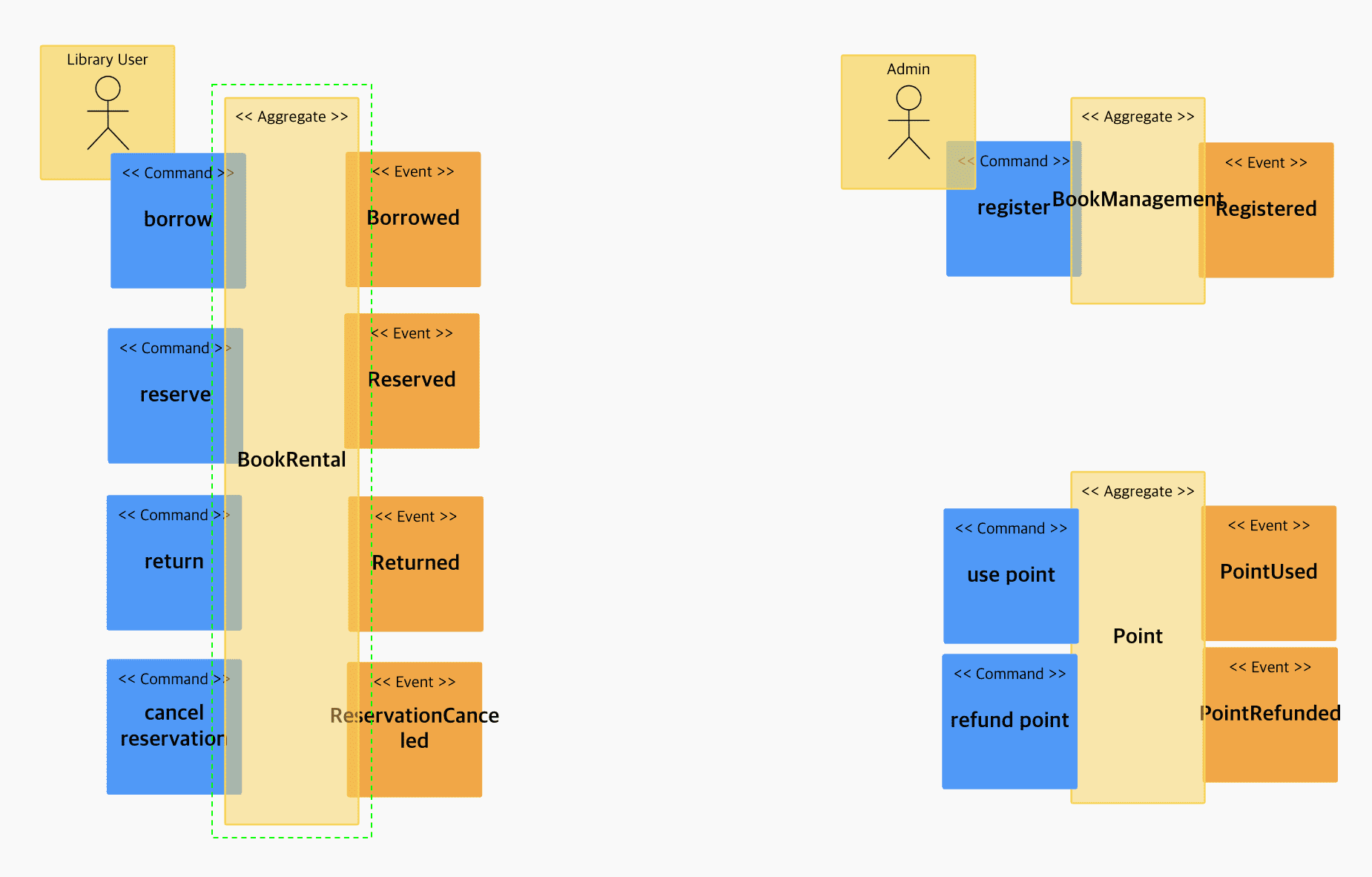
binding into aggregation
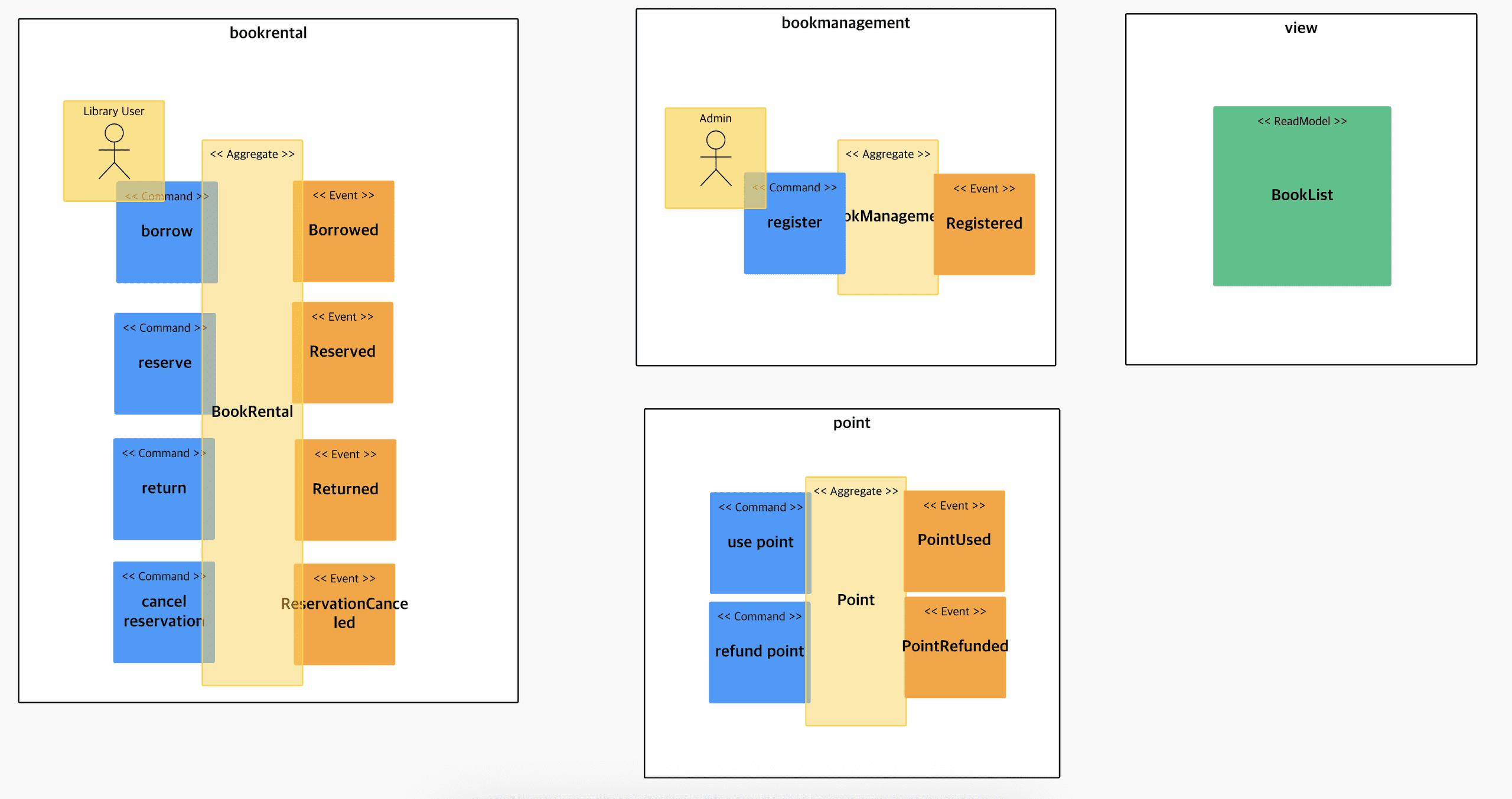
Binding into Bounded Context
-
Separation of domain sequence
- Core Domain: bookRental, bookManagement: Core service
- Supporting Domain: marketing, customer: Services to increase competitiveness
- General Domain: point: It is highly competitive to use a 3rd party external service as a payment service (to be converted to pink later)
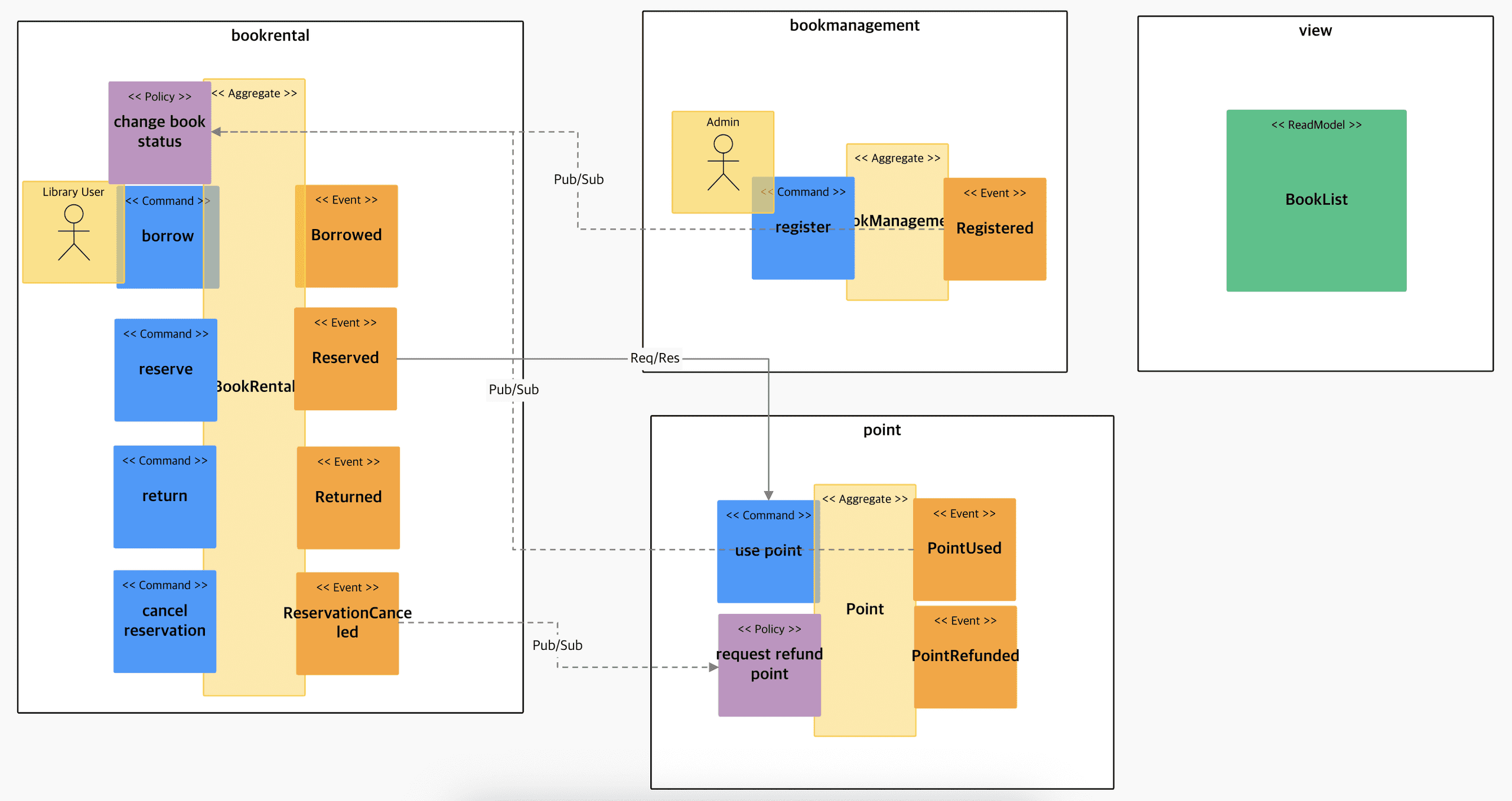
Attaching the policy
Policy movement and context mapping (dashed lines are Pub/Sub, solid lines are Req/Resp)
- Add View Model
Validate that functional/non-functional requirements are covered
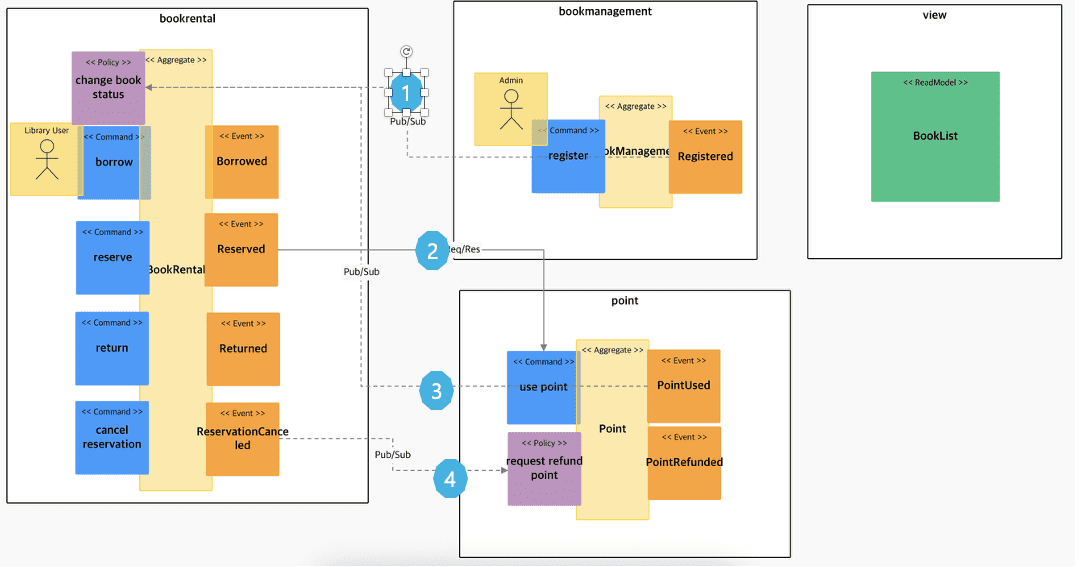
- The administrator registers the book. ok
- The user reserves the book. ok
- Points are used to reserve books. ok
- Points will be returned in case of cancellation of reservation. ok
- The user returns the book. ok
- User can cancel reservation (ok)
- If the reservation is canceled, the points are returned and the status of the book is changed to Canceled (ok)
- The user inquires the book status in the middle (addition of View-green sticker is ok)
- When a book is registered/reserved/cancelled/returned, the status of the book is changed and reflected in the entire book list. Both users and administrators can see this. ok
Verification of non-functional requirements
-
Transaction processing for scenarios that cross microservices
- Payment processing for book reservation: Request-Response method processing for point payment processing upon reservation completion
- Book status change when payment is completed: Transaction is processed in Eventual Consistency method.
- All other inter-microservice transactions: In most cases, the timing of data consistency is not critical, so Eventual Consistency is adopted as the default.
Hexagonal Architecture Diagram Derivation
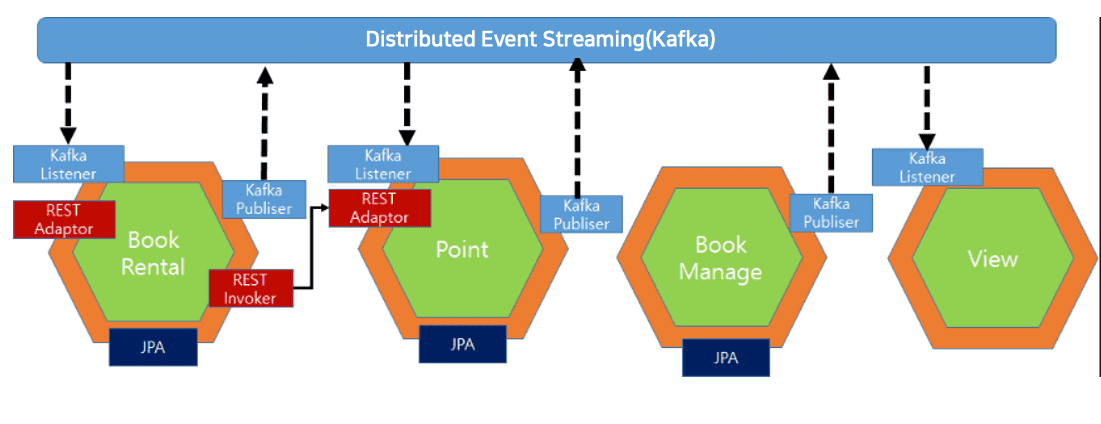
- Distinguish between inbound adapters and outbound adapters by referring to Chris Richardson, MSA Patterns
- Distinguish between PubSub and Req/Resp in the call relationship
- Separation of sub-domains and bounded contexts: Each team’s KPIs share their interest implementation stories as follows
Implementation
According to the hexagonal architecture derived from the analysis/design phase, microservices represented by each BC are implemented with Spring Boot. The method to run each implemented service locally is as follows (each port number is 8081 ~ 808n) bookManagement/ bookRental/ gateway/ point/ view/
cd bookManagement
mvn spring-boot:run
cd bookRental
mvn spring-boot:run
cd gateway
mvn spring-boot:run
cd point
mvn spring-boot:run
cd view
mvn spring-boot:run· Application of DDD
- Declare the core Aggregate Root object derived within each service as Entity. In this case, the language used in the field (ubiquitous language) is used as it is.
package library;
import javax.persistence.*;
import org.springframework.beans.BeanUtils;
import java.util.List;
@Entity
@Table(name="PointSystem_table")
public class PointSystem {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy=GenerationType.AUTO)
private Long id;
private Long bookId;
private Long pointQty =(long)100;
@PostPersist
public void onPostPersist(){
PointUsed pointUsed = new PointUsed(this);
BeanUtils.copyProperties(this, pointUsed);
pointUsed.publish();
}
public Long getBookId() {
return bookId;
}
public void setBookId(Long bookId) {
this.bookId = bookId;
}
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public Long getPointQty() {
return pointQty;
}
public void setPointQty(Long pointQty) {
this.pointQty = pointQty;
}
}- By applying Entity Pattern and Repository Pattern, RestRepository of Spring Data REST was applied to automatically create a data access adapter so that there is no separate processing for various data source types (RDB or NoSQL) through JPA.
package library;
import org.springframework.data.repository.PagingAndSortingRepository;
public interface PointSystemRepository extends PagingAndSortingRepository<PointSystem, Long>{
}- Testing of REST API after application
# bookManagement Service book registration processing
http POST http://52.231.116.117:8080/bookManageSystems bookName="JPA"
# bookRental Service reservation processing
http POST http://52.231.116.117:8080/bookRentalSystems/returned/1
# bookRental Service return processing
http POST http://52.231.116.117:8080/bookRentalSystems/reserve/1
# bookRental Service reservation cancellation processing
http POST http://52.231.116.117:8080/bookRentalSystems/reserveCanceled/1
# Check book status
http://52.231.116.117:8080/bookLists· Synchronous and asynchronous calls
As one of the conditions in the analysis stage, the call between reservation (bookRental) -> payment (point) was decided to be processed as a transaction that maintains synchronous consistency. The calling protocol allows the REST service already exposed by the Rest Repository to be called using FeignClient.
- Implement service proxy interface (Proxy) using stub and (FeignClient) to call payment service
# (app) pointSystemService.java
@FeignClient(name="point", url="http://52.231.116.117:8080")
public interface PointSystemService {
@RequestMapping(method= RequestMethod.POST, path="/pointSystems", consumes = "application/json")
public void usePoints(@RequestBody PointSystem pointSystem);
}- Process to request payment immediately after receiving reservation (@PostPersist) -> Since creation of BookRental occurs immediately after registering a book in BookManageSystem, payment is processed after reservation is received as a Post request.
# BookRentalSystemController.java (Entity)
@PostMapping("/bookRentalSystems/reserve/{id}")
public void bookReserve(@PathVariable(value="id")Long id){
PointSystem pointSystem = new PointSystem();
pointSystem.setBookId(id);
PointSystemService pointSystemService = Application.applicationContext.
getBean(library.external.PointSystemService.class);
pointSystemService.usePoints(pointSystem);
}
}After the payment is made, the act of notifying the book rental system is not synchronous, but asynchronous, so that the book status update is not blocked for the process of the book rental system.
- To this end, after leaving a record in the payment history, a domain event indicating that the payment has been approved is immediately sent to Kafka (Publish).
#PointSystem.Java (Entity)
{
@PostPersist
public void onPostPersist(){
PointUsed pointUsed = new PointUsed(this);
BeanUtils.copyProperties(this, pointUsed);
pointUsed.publish();
}
}The listener of the book rental system receives the payment completion event and changes the status of the book to reserved.
(BookRentalSystem) PolicyHandler.JAVA
{
@StreamListener(KafkaProcessor.INPUT) //When point payment is completed
public void wheneverPointUsed_ChangeStatus(@Payload PointUsed pointUsed){
try {
if (pointUsed.isMe()) {
System.out.println("##### point use completed : " + pointUsed.toJson());
BookRentalSystem bookRentalSystem = bookRentalSystemRepository.findById(pointUsed.getBookId()).get();
bookRentalSystem.setBookStatus("Reserved Complete");
bookRentalSystemRepository.save(bookRentalSystem);
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}When the book status is changed, an event called Reserved is issued.
BookRentalSystem.java (Entity)
{
@PostUpdate
public void bookStatusUpdate(){
if(this.getBookStatus().equals("Returned")){
Returned returned = new Returned(this);
BeanUtils.copyProperties(this, returned);
returned.publish();
}else if(this.getBookStatus().equals("Canceled")){
ReservationCanceled reservationCanceled = new ReservationCanceled(this);
BeanUtils.copyProperties(this, reservationCanceled);
reservationCanceled.publish();
}else if(this.getBookStatus().equals("Reserved Complete")){
Reserved reserved = new Reserved(this);
BeanUtils.copyProperties(this, reserved);
reserved.publish();
}
}
}Result: After the points are used, you can check the BookListView that the reservation has been completed and the status of the book has changed.

operation
· CI/CD settings
Each implementation was configured in their own source repository, the CI/CD platform used was azure, and the pipeline build script was included in azure-pipeline.yml under each project folder.
pipeline action result
In the image below, each service is uploaded to the azure pipeline so that it is automatically built/deployed whenever the code is updated.

As a result, you can see that the service is up on the kubernetes cluster as shown below.

Also, it can be seen that the functions operate normally.






· autoscale out
- Configure HPA to dynamically increase replica for point service. The setting increases the number of replicas to 10 when CPU usage exceeds 15%:
- Monitor how the autoscale is going

- After running the workload for 2 minutes, the test results are as follows.

· Uninterrupted redistribution
After the autoscaler setting and readiness was removed, load was applied. After that, I updated the code that removed Readiness and started deploying it as a new version. The result is as below.


I put the Readiness setting again and put the load in. And after deploying the new version, the result is as follows.


Uninterrupted redistribution is confirmed to be successful because availability does not change during the distribution period.

